Due to its illicit history, there is less documented research on how to safely produce Cannabis sativa that is safe for consumption while retaining its additional qualities. Producing a disease-free product is made more difficult by the long drying and curing time Cannabis stavia requires.
Each grower has different processes, but here is one example that gives an idea of the lengthy timescales involved:
| Step | Parameters | Time |
| Phase 1 drying | 20°C (68°F) RH of 55% | 3 days |
| Phase 2 drying | 18°C (64°F) RH greater than 50% | 1-2 weeks minimum, 3 weeks maximum |
| Curing | 18°C – 21°C (64°F – 70°F) RH 50% – 55% In complete darkness | 4-8 weeks or longer |
The product needs to dry and cure for weeks or months in a warm and relatively humid environment, giving plenty of opportunities for pathogens and spoilage microorganisms to propagate.
One documented solution for producing safe Cannabis is chemical biocides. There are still many regulatory restrictions on these, but there is a sense of urgency to test them for safety and efficacy.
Physical interventions, like UVC and heat are another popular safety mechanism because they are already cleared for use by the FDA, and do not use chemicals. However these interventions are required to be non-thermal and dry to decrease risk during the drying and curing phase. One such physical method is using gaseous ozone, which does not cause an increase in antimicrobial resistance. Gaseous ozone inactivates bacteria, fungi, and viruses, but it is vital to keep the concentration very low to avoid affecting the product. It has been proved effective at fighting common diseases impacting Cannabis sativa.
The most common diseases facing Cannabis sativa include:
- White Powdery Mildew (Golovinomyces fungus)
- Gray Mold (Botrytis fungus)
- Fusarium Wilt and Root Rot (Fusarium fungus)
Most research points to preventative care being the best way to manage them, including deep cleaning:
- Hands
- Tools
- Containers
- Clothes and footware
- Water
- Machinery
Chemical cleaning methods are common, but never have 100% coverage, and growers are looking at other methods like non-thermal dry autoclaves large enough to hold entire pallets and whole machinery.
Safety and Quality: EPIC iO Low and Slow
EPIC’s approach is to use super-low concentrations of pulsed ozone gas. This allows us to modify the atmosphere of the drying and curing room without introducing chemicals or altering the temperature and humidity. The low concentrations work over a long period to inactivate pathogenic spoilage bacteria, fungi, and viruses, without affecting the qualities of the underlying product.
EPIC iO AURA™ is an ozonating device the size of a briefcase and simply plugs into a regular outlet, and tracks temperature, relative humidity, and the vapor pressure deficit (VPD – more on that below), while providing you with regular reports and alerting you to any red flags.
Yield and Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD)
The best growers know that plant transpiration directly affects yield. Monitoring VPD helps identify the correct range of temperature and humidity to use in the grow space, and it reduces pest and environmental problems.
In a nutshell, VPD is an indicator of how much more space is there for water vapor in the air. If it’s too dry, there’s too much space and this causes stomata to shrink to protect itself, carbon dioxide uptake decreases, the plant gets stressed and yield goes down. At the same time, the plant increases its rate of transpiration and nutrient uptake. Bottom line, monitoring temperature and humidity to control VPD is critical to the balancing act every grower must perform.
EPIC iO uses Internet of Things (IoT) to measure temperature and relative humidity every few seconds. Using complex charts we calculate the theoretical saturation vapor pressure (SVP), which is the maximum possible, and the actual vapor pressure (AVP), and derive the VPD from the difference.
The optimum VPD range is between 0.8 and 1.2 kPa. Growers use a wide range of relative humidity’s from 30% to 62%, but with the majority being in the 55-62% range.
You can see in the chart from EPIC iO’s DeepInsights™ how dramatically the VPD changes with relative humidity. Merely opening a door from an air-conditioned room can cause relative humidity to suddenly drop by 20-30%.
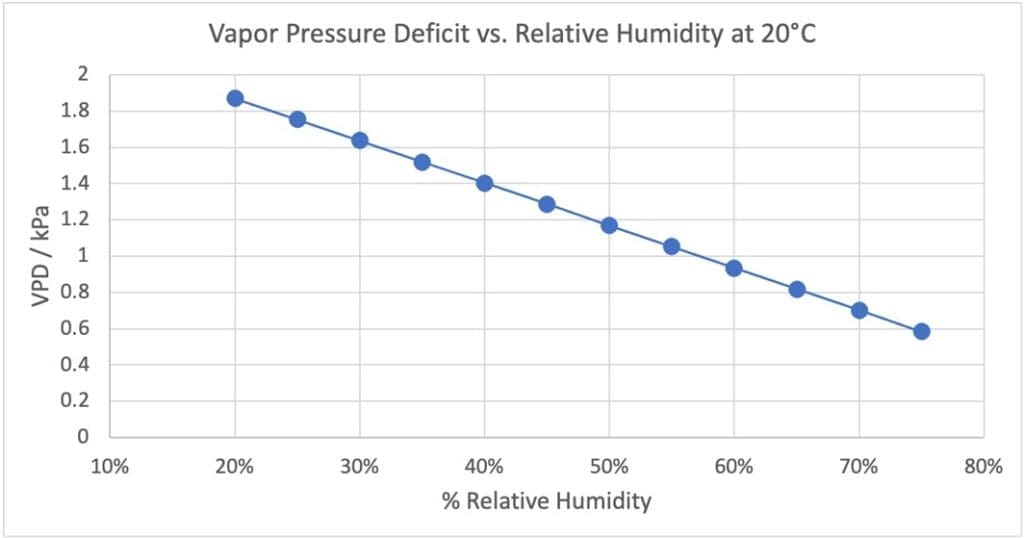

EPIC iO’s Enterprise Biosecurity solutions directly addesses the challenges cannabis growers face. We provide a modified Ozone solution to combat pathogenic food safety as well as the many fungal and bacterial microorganisms that cause loss through spoilage. Additionally, our IoT sensors help to manage the growing environment to help growers maximize their yield.
To find out more about how we can help you maximize your business, contact us.
Supporting evidence
SVP = 0.61078 x e^(17.2694 * T / (T +237.3) ) kPa
T is in degrees Celsius
AVP = SVP * RH/100
VPD = SVP - AVP








